LED Lighting Jargon Buster
What is LED and why choose it?
In LED lighting, LED stands for “Light Emitting Diode”.
An LED is an electrical component which converts electricity into light with very little wasted energy. LED lights combine several of these components to produce a light source suitable for general use.
LEDs have a lifespan of more than 30,000 hours and use little energy, meaning they pay for themselves with savings on electricity bills. Compared to the old incandescent light bulbs, LEDs can save up to 90% in energy consumption.
Throughout this article we will refer to light source. Basically, we are referring to the bulb, lamp, or spotlight – where the light is coming from.
OK, so what’s an incandescent and what’s a halogen?
You may still have incandescent and halogen bulbs in your house – but the likelihood is that when you go to replace these, what you buy will be an LED.
Incandescent bulbs work when an electric current passes through thin filament wire, heating it until it glows. Heat radiates outward, but only a small portion of that energy is converted into usable light. Halogen bulbs are similar to incandescent bulbs but with some minor differences – they have a filament wire, but unlike incandescent bulbs, a small amount of halogen gas in the container mixes with vapour from the filament and deposits back onto the filament. The process extends the bulb’s lifespan and allows it to work at a much higher temperature than incandescent bulbs, which increases light output.
However, this process makes both types of bulbs energy inefficient compared to LED.
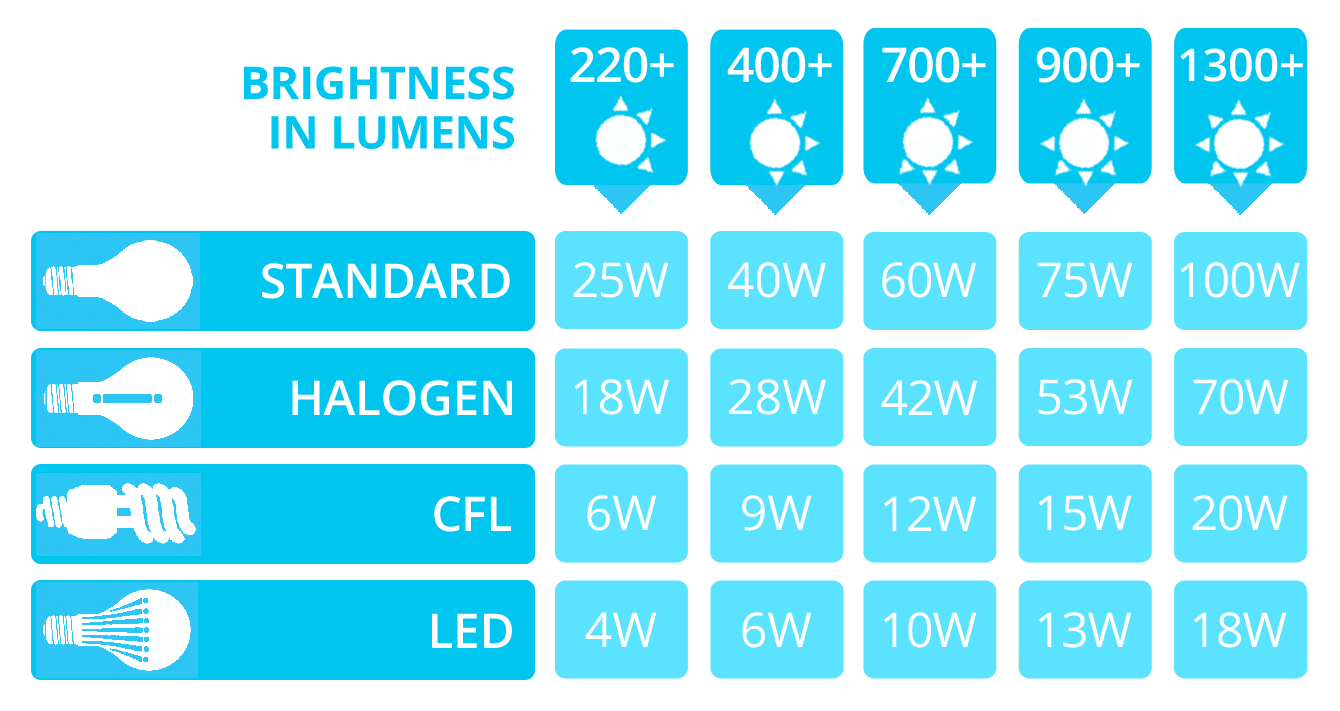
What about the “energy saving” bulbs?
What you may know as “energy saving bulbs” are called CFL bulbs in the industry. Unlike incandescent and halogens, they don’t have a filament; instead, they use an electric current to excite gases within the bulb that then cause a phosphorous coating on the inside of the bulb to glow, producing light.
Although they are more efficient than incandescent lighting, CFLs are less efficient than LED and last only 8,000 hours compared with more than 30,000 hours for a typical LED source.
You will also notice that they take a while to warm up, so they are not great for bathrooms or stairways. They are also quite strangely shaped so may not fit into your light fittings very well.
Bulb versus Lamp
These terms are used interchangeably and generally mean the same thing, although those in the lighting industry would say that bulbs are things you put in the ground! Anyway, these are general terms used to describe a small to medium light source and its housing.

Fitting Types
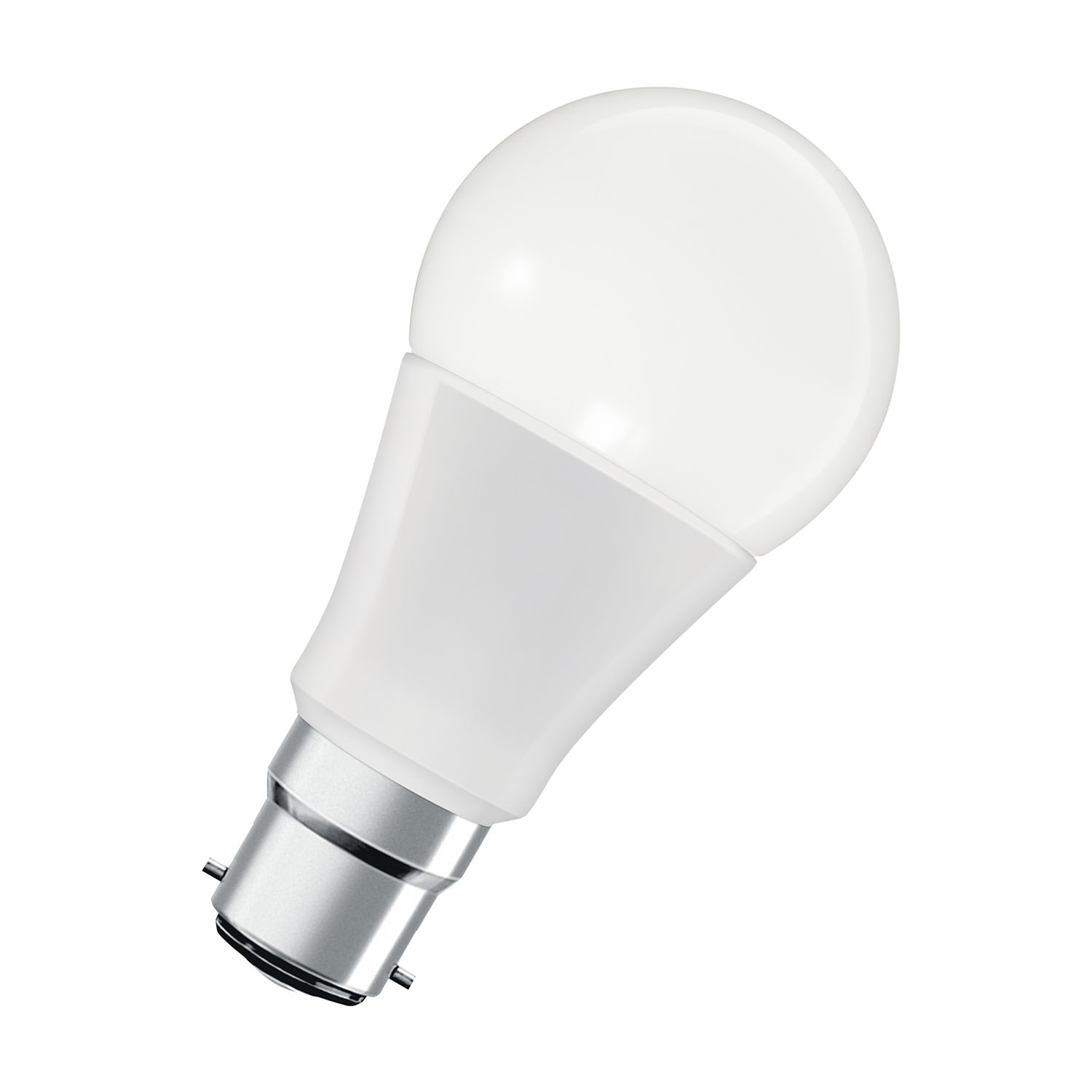
Bulbs
Bayonet Cap
Bayonet cap bulbs are placed in the fitting and then twisted to secure it – we know these as traditional bulbs that are found in the shade hanging from the ceiling. They can also look like vintage-style filaments.
Bayonet caps come in two sizes, B22 and B15, sometimes referred to as BC (Bayonet Cap) and SBC (Small Bayonet Cap). The B in B22 and B15 stands for bayonet, while the 22 and 15 stand for 22mm and 15mm. These measurements refer to the diameter of the bayonet fitting.
See our Bulb Finder for more information.

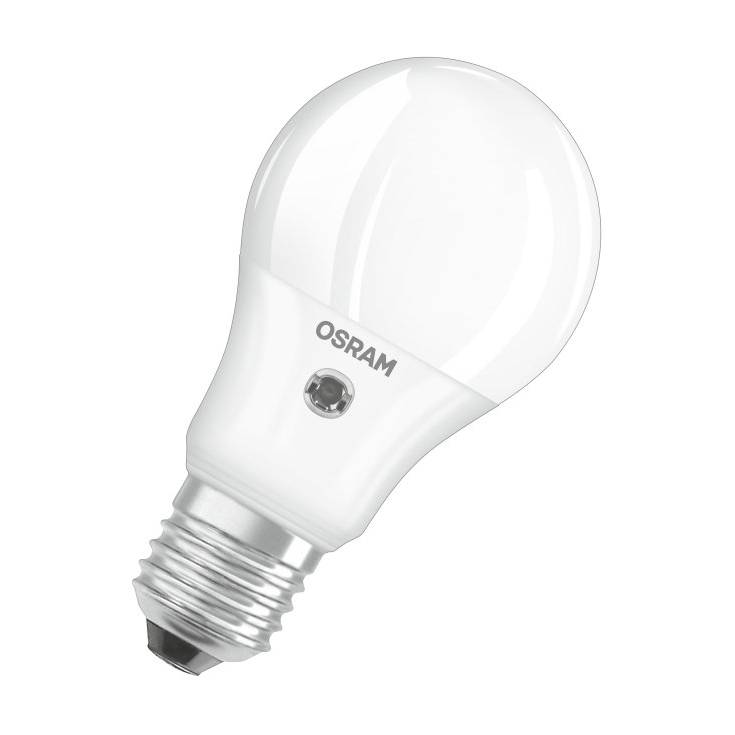
Edison Screw
Edison Screw is a type commonly found on light bulbs that screw into a fitting – usually found in decorative floor or table lamps.
Edison Screw bulbs come in two sizes, E27 and E14, sometimes referred to as ES (Edison Screw) and SES (Small Edison Screw). The E in E27 and E14 stands for Edison, while the 27 and 14 stand for 27mm and 14mm. These measurements refer to the diameter of the screw connection on the bulb.
See our Bulb Finder for more information.

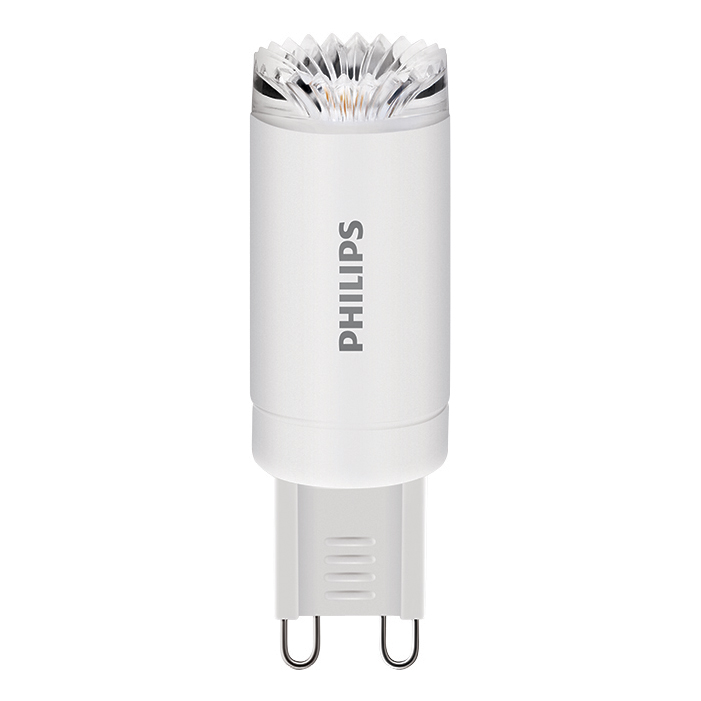
Capsules
Capsules are the type of fitting you will find in decorative lamps – they will have two metal pins that you push into a fixture. Capsules come in two sizes, G9 and G4. The G in G9 and G4 refers to the fact these have pins, and the 9 and 4 stands for the distance between the pins – 9mm or 4mm.

Spotlights
GU10
GU10 is a common spotlight fitting comprising of two metal prongs that twist into a fixture. The 10 in GU10 refers to the distance in mm between the two prongs. GU10s are usually used in the kitchen, lounge, or bathroom.
See our Bulb Finder for more information.

MR11 (GU4)
MR11 is a type of spotlight fitting with two thin metal prongs which are pushed into a fixture. Uncommonly referred to as GU4s, the 4 in GU4 refers to the distance in mm between the two prongs.
You could find these in your bathroom or kitchen, because they are low voltage. As these type of areas can be wet or humid, it is safer to have a light which is lower voltage in case of any faults.
See our Bulb Finder for more information.

MR16 (GU5.3)
MR16 is a common spotlight fitting with two thin metal prongs which are pushed into a fixture. Uncommonly referred to as GU5.3s, the 5.3 refers to the distance in mm between the two prongs. This type of light is bigger than a MR11, but still low voltage and therefore most likely to be used in your kitchen or bathroom.
See our Bulb Finder for more information.

Downlight
Downlights are enclosed units which combine a fixture housing and a light source all in one, so that’s the metal or plastic surround you see on the ceiling, the spotlight and the casing within the ceiling. You can buy downlights that contain any type of spotlight.
They are commonly fitted directly in the ceiling plasterboard – so traditionally would be what you buy when renovating a room or property.

2D replacements or bulkheads
You may hear these terms when someone is referring to outside or bathroom lighting. In technical terms, 2D is the actual lamp itself and the bulkhead is the fitting this goes into but the two terms are both commonly used.

Technical Talk
Energy and measurement
Watt (W)
The recognised measurement of power. In lighting, watts measure the amount of energy drawn by the light source.
Equivalent Wattage
LED lighting requires much less power than conventional incandescent lamps. Equivalent wattage is the power an incandescent lamp would need to run at to be as bright as the comparable LED lamp. For example, the equivalent wattage of a 6W LED bulb is commonly a 50W incandescent bulb.
Kilowatt Hour (kWh)
A kilowatt is 1000 watts. Kilowatt hour is a unit of energy for watts used over time. One kilowatt hour is 1 kilowatt used for 1 hour. For example, a 1000 watt heater, used for two hours, would use 2 kWh in energy. Utility companies commonly measure domestic usage in kWhs.
A 60W incandescent light used for four hours a day would use 0.24kWhs. Whereas a 9W LED light would only use 0.036kWhs in four hours.

Lumen (Luminous Flux)
The recognised measurement of total light emitted from a source (luminous flux), i.e. the total amount of light emitted. The higher the lumens the more light it emits. Although you may see this listed on a product, it will only generally need to be a consideration in places such as museums and galleries. But, if you prefer an extremely well-lit area in your home, we recommend choosing a light with a high lumen rating.
Efficacy (Luminous Efficacy)
Efficacy can be roughly described as how energy efficient a light source is. It describes how much light you get out from the power you put in. It is a ratio of lumens (total light emitted) to power, for example, 90lm/W (90 lumens per watt).
The higher the number of lumens compared to the power, the greater the efficacy, and therefore the more energy efficient. So again, if you are looking for a light that’s going to be really energy efficient, choose the option with the highest lumens per watt.
Look & feel jargon
Beam Angle
The measure of how far light spreads over a given area from a lamp – it is measured in degrees.
A large number covers a large space while a small number will create a narrow spot of light. Although you may see this listed on a product ,it will only generally need to be a consideration in places such as museums and galleries – unless, for example, you want to light a piece of artwork in your home.

Colour Rendering Index (CRI)
A scale varying from 0 to 100 which describes how accurately colours appear under a light. The higher the number the better. For example, under a low CRI – below 60 – green objects can appear brown. A high CRI lamp will display the object as green.
High-quality LED lights above 95 CRI are well suited to environments where rendering colours accurately is important, such as museums and galleries.

Colour Temperature
Measured in Kelvin (K), this describes how the light looks, often phrased as ‘warm’, ‘white’, and ‘cool’. Measurements vary from 1900K for very warm to 5000K+ for very cool lights.
Warm White lighting will appear golden and yellow in colour, similar to a burning candle.
White lighting appears white.
Cool white describes a colour temperature of 4000K+ which appears slightly blue
Dimmable
This means your lights can be dimmed to different intensities by using a dimmer switch. If you change your bulbs to LED, you will also need to update the dimmer switch on your wall or move to a normal switch. This is because the dimmer used for halogens and incandescent will not be compatible.

Safety talk
IP Rating
Stands for: Ingress Protection marking.
The IP rating indicates how resistant a fitting is to irritants. Areas that are often wet or dusty need higher IP rated products.
IP ratings consist of two numbers, e.g. 65. The first number (from 0 to 6) refers to how well the fitting is resistant to solid particles, like dust. The second number (from 0 to 9) refers to how resistant the fitting is to liquids.
The higher the number the more resistant the fitting is, with IP65 ratings suitable for outdoor uses.
Life (Rated Life / Life Span)
This is an indication of the lifespan of the bulb and is given in hours.
PIR Sensor
Stands for: Passive Infrared Sensor.
These sensors monitor movement in a room and automatically turn on lighting when people are present, and off again when nobody is there. They are more commonly referred to as motion sensors. They help reduce consumption by ensuring lights are turned off when they are not needed, and you will commonly find these on outdoor security lights.

See our full range of domestic & commercial lighting
0333 123 5464



