Energy saving in context – infographic views of lighting consumption
Written by Tim Greenhalgh
Posted on October 8, 2014
We picked up two infographics this week that put energy saving in context, showing lighting consumption and potential benefits of reduction.
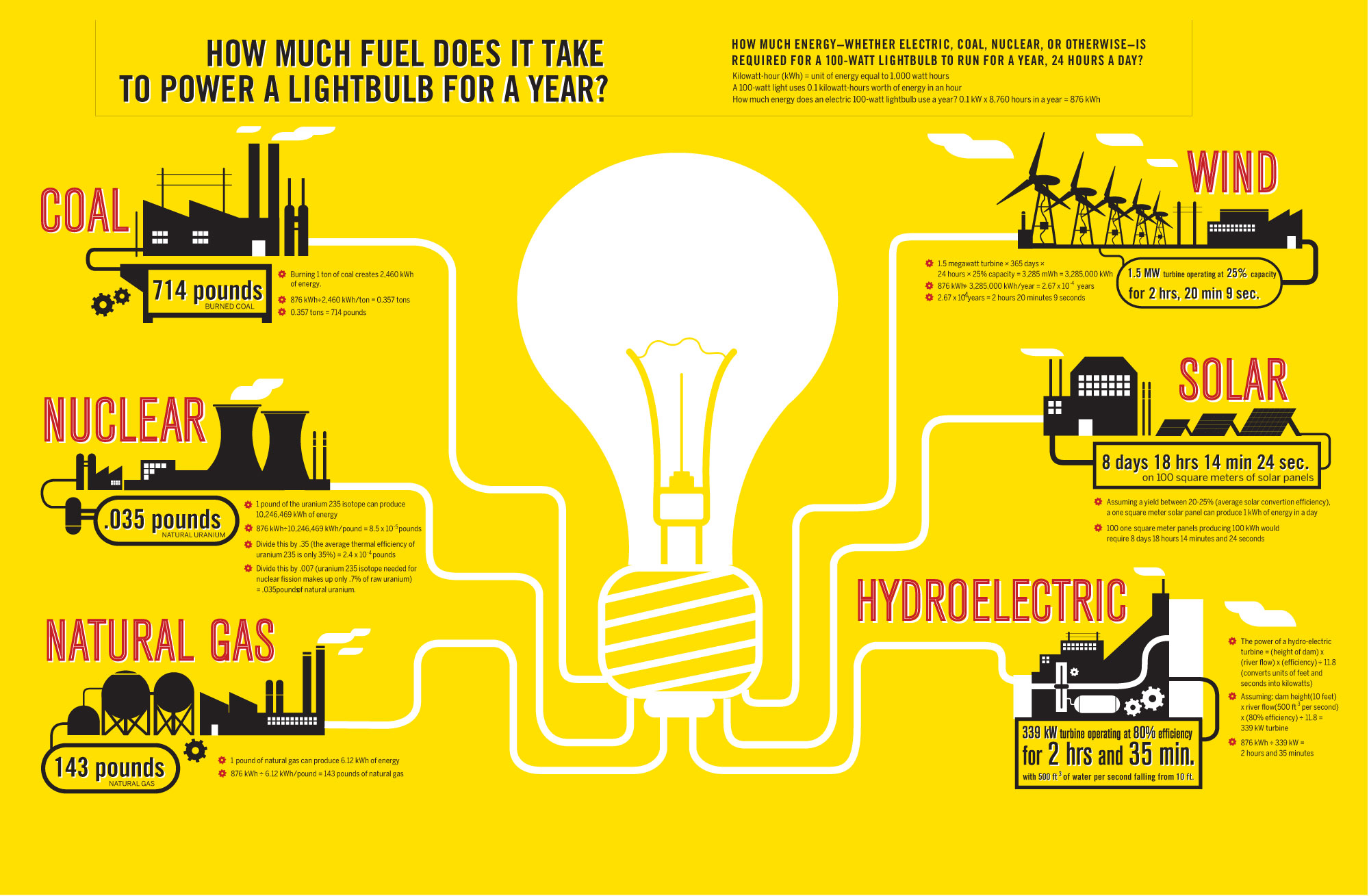
The first infographic elegantly shows the varied energy production sources and what would be needed for each to keep a traditional lightbulb burning for a year, from 714 pounds of coal to .035 pounds of uranium to 2 hours 20 minutes of a 1.5 mW wind turbine rotating at 25% capacity.
Lux magazine provided the second infographic and reinforced our long-voiced appeal for substantial government intervention to reduce energy usage in lighting.
Lux says: “Unless something is done, we risk suffering blackouts at times of peak demand, according to warnings from the Royal Academy of Engineering and the National Grid.
Following years of underinvestment, the government’s plan to address the issue is to increase capacity, with more nuclear and more renewables – both controversial solutions, and both with their own set of challenges to overcome. But what if there were another way? What if you could avoid boosting supply by slashing demand?
Lux decided to take a look at the impact that energy-efficient lighting could have on the 316 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity that the UK uses each year.

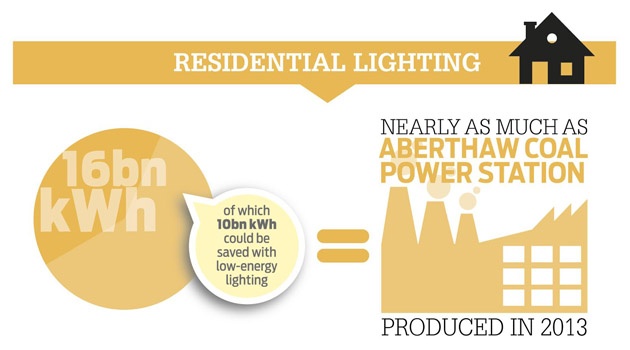
If every home adopted LED lighting, the energy savings would be massive with comparative savings in carbon emissions.
Energy costs will continue to rise – average bills have risen by more than a third over the past three years – so concerted action at national level is clearly needed to encourage households and businesses to invest in energy-saving LED lighting.